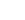
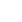The ejector pump, a highly efficient fluid-handling device, is gaining widespread recognition across multiple industries due to its unique design and operational advantages. As businesses increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, the ejector pump has become a preferred choice for applications in wastewater management, chemical processing, refrigeration, and beyond. With no moving parts and small maintenance requirements, this technology offers a cost-effective and reliable alternative to traditional pumping systems.
At its core, an ejector pump utilizes the Venturi effect, where a high-pressure primary fluid accelerates through a nozzle, creating a low-pressure zone that draws in and transports a secondary fluid. This mechanism allows the ejector pump to handle liquids, gases, and mixed-phase flows without the need for mechanical components. The absence of rotating parts significantly reduces wear, extending the pump’s lifespan and lowering operational costs.
Ejector pumps are particularly effective in environments where conventional pumps struggle, such as in corrosive, high-temperature, or particulate-laden conditions. Their simple yet robust design makes them suitable for demanding industrial applications where reliability is critical.
One of the many compelling advantages of ejector pump systems is their energy efficiency. Unlike traditional pumps that consume substantial power to maintain flow rates, ejector pumps require only a steady supply of motive fluid, reducing overall energy consumption. This aligns with global efforts to less carbon footprints and optimize industrial processes.
Additionally, ejector pumps are highly versatile. They can be used for pumping, mixing, compressing, and even vacuum generation, making them indispensable in sectors like oil and gas, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. Their ability to handle abrasive and viscous fluids without clogging further enhances their appeal in challenging operational environments.
In wastewater treatment plants, ejector pumps play a crucial role in moving sludge and aerating tanks. Their clog-resistant design ensures smooth operation even when handling solids and high-viscosity fluids. Municipalities and industrial facilities are increasingly adopting ejector pumps to improve system longevity and reduce maintenance expenses.
The oil and gas industry utilizes ejector pumps for vapor recovery, gas compression, and pipeline boosting. Their ability to operate in hazardous environments without spark risks makes them a safer alternative to electrically driven pumps. Furthermore, their efficiency in handling multiphase flows enhances productivity in extraction and refining processes.
Ejector pumps are being integrated into modern HVAC and refrigeration systems to improve thermal efficiency. By recovering waste heat and optimizing refrigerant circulation, these pumps contribute to energy savings in commercial and industrial cooling applications. Research is ongoing to expand their use in next-generation sustainable cooling technologies.
Emerging applications in geothermal and solar thermal energy systems highlight the ejector pump’s potential in renewable energy. By facilitating efficient heat transfer and fluid circulation, these pumps support the development of cleaner energy solutions.
As industries continue to seek sustainable and cost-efficient technologies, the ejector pump market is expected to expand significantly. Advances in materials science, such as corrosion-resistant alloys and composite materials, are further enhancing the durability and performance of ejector pumps. Researchers are also exploring hybrid systems that combine ejector pumps with other technologies to improve efficiency.
With regulatory pressures pushing industries toward greener practices, the demand for low-maintenance, energy-saving solutions like ejector pumps will likely accelerate. Their adaptability across diverse sectors positions them as a cornerstone of modern fluid-handling systems.
The ejector pump represents a smart, sustainable alternative to conventional pumping mechanisms. Its efficiency, durability, and versatility make it an ideal solution for industries striving to reduce operational costs and environmental impact. As technological advancements continue to refine ejector pump designs, their role in shaping the future of industrial fluid management will only grow more prominent.

 English
English русский
русский عربى
عربى